Ping An Insurance (2318.HK): China's Insurance and Technology Giant
The insurance power house and (quite) digital giant of China
Summary
Solid Market Position: One of the largest insurer in the world by market cap, maintaining a leading market share in most product lines; strong brand recognition
Diversified Ecosystem: Unique integrated ecosystem of services, such as life, property, auto and healthcare insurance; massive customer base of 227 million
Tech-Savvy Organization: Embracing the use of innovative technologies such as AI and cloud computing) to enhance its capabilities in pricing, cross-selling, customer development and operational efficiency; ranked 3rd globally with AI patents
Healthy long-term Profit Growth and ROE: L&H insurance business and banking segment with YoY growth rates of 16% and 25% in 2022, respectively; L&H segment with remarkable ROE of 32.7%
Attractive Dividend: Dividend growth of 26% CAGR (10y) and payout ratio of around 30%
Aging Population and Low Insurance Penetration: Untapped market potential with insurance penetration rate around 4.5% in 2021 and low insurance density of around $275, presenting significant avenues for growth
Introduction of Ping An Insurance
Ping An Insurance (Group) Company of China, Ltd. (hereafter “Ping An” or the “Company”), was founded in 1988 as a property and causality company. Since then, it has evolved into one of China's foremost financial services providers, and it was ranked 17th on the Forbes Global 2000 list in 2022. Headquartered in Shengzen (China) the company went public in 2004 with its listing on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange (HKEX:2318) which was the largest initial public offering (IPO) in that year, followed by a listing on Shanghai stock exchange (SHA:601318) in 2007, marking the world's largest IPO for an insurance company at that time.
Born small with no state-capital background, Ping An has risen to become one of China's top three integrated financial conglomerates. Over the course of several decades, the company has undergone a notable transformation, from a traditional insurance company to a technology-driven enterprise, adding wealth management, banking, auto, health to its ecosystem.
Born from humble beginnings, who is Ping An now?
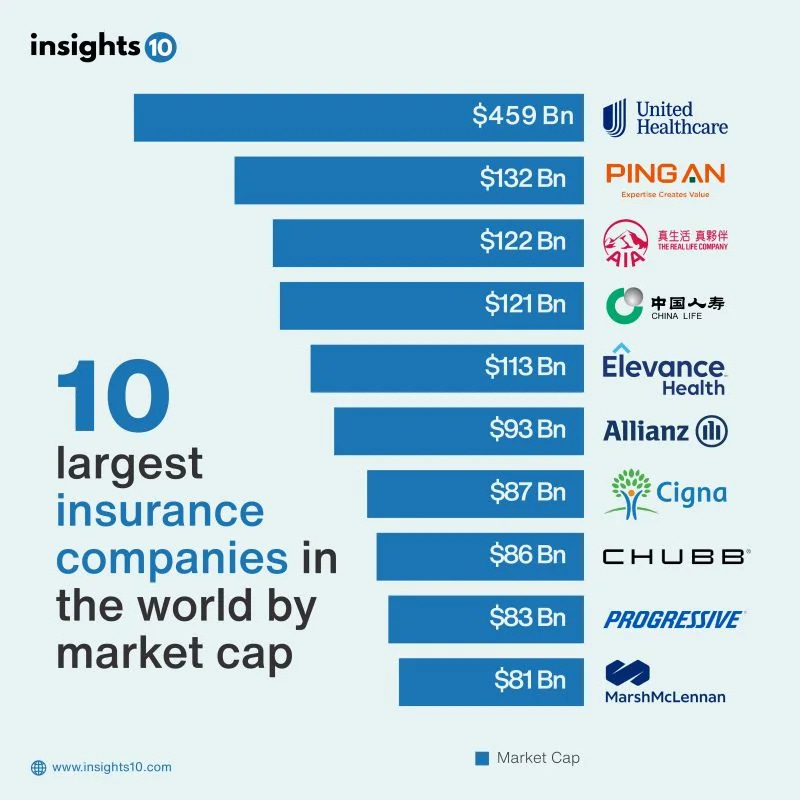
Today, Ping An holds the position oft the second highest-ranked insurance company in the world by market cap, though it has faced more challenges in the last year compared to numerous peers from United States and Europe.
Ping An operates mainly in China and in addition to its core insurance business, the company offers banking, auto services, asset management and healthcare services via following five business segments
Life and Health Insurance (L&H)
Property and Casualty Insurance (P&C)
Banking
Asset Management
Technology
The main business segments including L&H, P&C, and banking make up the bulk of Ping An’s revenues with smaller contributions seen from its securities, technology and other asset management segments.
Beneath the surface, Ping An's masterstroke lies in its ecosystem strategy - emphasizing "integrated finance" and "healthcare. " At the heart of this strategy lies the development of its ingenious "one customer, multiple products, and one-stop services" model. The company offers a diverse array of financial and healthcare services through its integrated ecosystems, and creates a closed-loop of offerings that envelops the customer on the platform.
Beyond the boundaries of Ping An’s traditional insurance business [Moat #1]
Ping An stands out from conventional insurance companies due to its persistent commitment to innovation and substantial investments in cutting-edge technologies like AI and cloud computing. While maintaining its core focus on financial and insurance services, the company places a strong emphasis on developing and integrating core technologies, positioning itself as a prominent leader in the tech industry. The company's unwavering dedication to innovation is clearly demonstrated by its esteemed global ranking in patent applications related to AI, fintech, and digital healthcare.
In 2021, the company outperformed tech giants such as Microsoft and Alphabet in terms of active AI and machine learning patent families, cementing its position as a leader in cutting-edge technology.
Ping An held an impressive record in technology patent applications, surpassing most international financial institutions with a total of 46,077 applications at the end of 2022, an increase of 7,657 from the beginning of the same year.
While maintaining a strong foundation in insurance, the company has evolved into a multifaceted financial services company and created numerous technology-driven spin-offs that extend well beyond its traditional business scope, many of which have been developed organically.
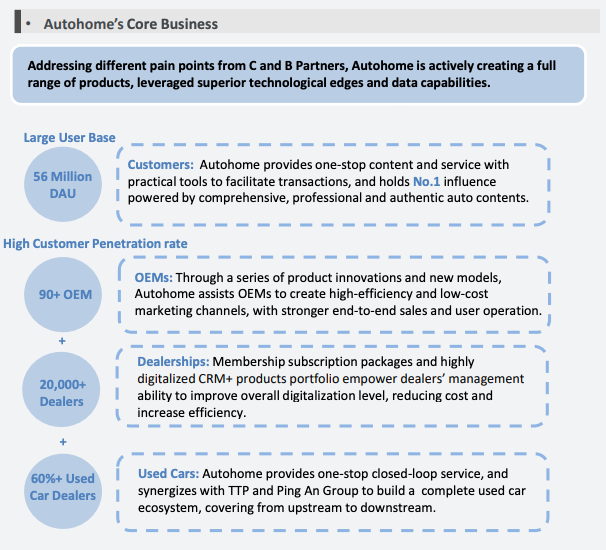
Autohome
Headquartered in Beijing, Autohome (NYSE: ATHM; SEHK: 02518.HK) is a leading online vehicle marketplace, boasting 19 thousand paying dealers and consistently draws in over 50 million daily page visitors through its web portal. The core revenue streams for the company predominantly stem from advertisements and fees collected from both automakers and dealers. This revenue model underscores Autohome's strong positioning in the online vehicle marketplace, reflecting its ability to attract substantial user engagement and provide value to industry stakeholders.
Autohome played a significant role in China's used passenger car transaction volume, contributing approximately 21.5% in 2022, as reported by the China Automobile Dealers Association. Over time, Autohome expanded its reach by acquiring TTP Car Inc., China's top online used car auction platform, after making an initial investment in 2018.
Lufax
As the largest fintech spinoff of Ping An Group, Lufax (NYSE: LU) is a leading technology-empowered financial services enabler for small business owners (SBO) with a cumulative total of 19 million borrowers of the close of 2022.
Lufax distinguishes itself as a non-traditional service provider enabling financing transactions by connecting banks with previously unreached SBO’s and other borrowers. For example, the company uses AI-powered credit assessment capabilities where the borrower is assessed based on automatic speech and optical character recognition. Lufax also gains a significant advantage from its strong ties to the Ping An ecosystem, utilizing a vast database of customer data for sourcing investors and borrowers.
OneConnect
OneConnect (NYSE: OCFT; SEHK: 06638.HK) provides cloud-based technology services for small to medium-sized banks and insurance companies and has demonstrated its wide-reaching influence in the Chinese financial sector. By June 2020, the company had successfully served all state-owned banks and joint-stock banks in China, as well as 99% of commercial banks and 53% of insurance companies.
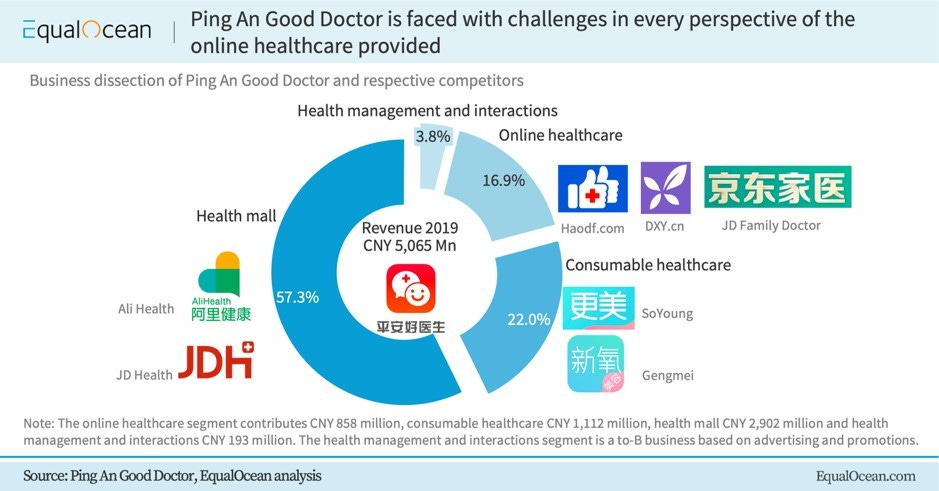
Ping An Health (or Ping An Good Doctor)
Ping An Health is a digital health platform addressing the challenge of limited and uneven distribution of high-quality healthcare services in China. It is committed to build a one-stop ecosystem platform and a professional bridge between doctors and patients providing membership based healthcare services. Four key segments of the business are:
Online medical services
Consumer healthcare
Online Mall for drugs
Health management and wellness interaction
With cumulative paying users over 43 million by the end 2022, Ping An Health is a key player in the digital health space in China.
Unique Cross-Selling Opportunities via Ping An’s Ecosystem [Moat #2]
So, how does all this technological advancement, ecosystem with integrated products and services, and massive customer base plays out ?
As of end of 2022, Ping An had a total of 227 million retail customers holding multiple contracts across their subsidiaries. Notably, over the past three years, there has been a favourable trend in the customer profile, marked by a substantial rise in customers with contracts lasting five years or longer.
Moreover, as customers stay with Ping An for longer periods, they tend to hold more contracts as well. From 2022, contracts per retail customer increased by 2.1%, reaching an average of 2.97 contracts.
This loyal customer base not only offers Ping An valuable insights into customer needs but also fosters long-term relationships, resulting in a significant increase in cross-selling capabilities. As of end of 2022, over 90 million retail customers held multiple contracts with different subsidiaries, demonstrating a growing product stickiness and loyal customer base, more importantly showcasing the benefit of owning an ecosystem.
Additionally, In 2022, the income per agent generated from cross-selling experienced an impressive 50% YoY growth, making a significant contribution to the overall performance and productivity of the agents and attracting new recruits by solidifying Ping An's unique position as a leader in the industry.
It's crucial to highlight that Ping An's ongoing technology investments spanning the past decades have been instrumental not only in shaping product and service development, but also in enhancing internal operational efficiency across its core sectors. By seamlessly integrating data across its subsidiaries, Ping An efficiently reaches new clients with reduced customer acquisition costs, thus propelling accelerated business expansion and heightened profitability within its core insurance operations.
Ping An's tech-driven ecosystem, the intricate integration of technology into its core operations, and deserve much more coverage. However, these aspects will be incorporated into the forthcoming revisions and updates on Ping An, providing a deeper insight into how technology has revolutionized the company's operational landscape.
Management
Ping An was founded in 1988 by Peter Ma. Peter, who remains the Chairman and CEO of the company, is also the originator of the guiding vision for the company's development. At Ping An, the top management team comprises individuals with a substantial number of non-traditional financial backgrounds. This diversity also explains, in part, why Ping An was able to explore new business models and technologies much more aggressively.
To spotlight a key figure within Ping An, Jessica Tan, a graduate of MIT and former partner at McKinsey, played a crucial role in transitioning Ping An's IT systems to the cloud. Joining the company in 2013, she later became one of the Co-CEOs under Peter Ma's leadership in 2018. This strategic shift to the cloud enabled Ping An to pioneer advanced data analytics and adopt artificial intelligence, cementing its position as a technology-driven enterprise.
For those interested in delving deeper into Ping An's management quality, vision, and technological advancements in more detail, the additional links provided under further readings are definitely worth checking out. It's also worth noting here Michael Fritzell's write up on Ping An, which delves into Ping An's dynamics, including risks and relationships with the Chinese Communist Party (CCP).
Industry & Business Environment
In 2021, despite economic uncertainty and challenges, the global insurance industry witnessed significant growth, with total premium income surpassing $6.8 trillion while the top 20 markets collectively contributed to nearly 90% of this global insurance market.
As per the Allianz global insurance report for 2022, insurance premiums are expected to undergo a consistent annual rise of 5.2% in the coming decade. This sustained growth is projected to contribute a remarkable $4 trillion to the global premium pool, with the combined premium income estimated to reach more than $9 trillion by the year 2033.
Taking a closer look at the Chinese insurance landscape, it comprises two key segments: life insurance and non-life insurance, encompassing areas like auto, property, and casualty coverage. Over the past two decades, the market has experienced significant expansion, driven by rapid economic growth, an increasing middle class, and rising awareness of insurance products among the Chinese population. China's life insurance premium is projected to surpass the US market and emerge as the world's largest market by 2030 according to a report Oliver Wyman Partner. The report forecasts significant growth with an estimated annual increase of up to 13% once the country's disposable income per capita reaches the tipping point of US$7,000-10,000.
Looking ahead to the year 2050, the Chinese insurance market size is projected to soar to an impressive RMB 45 trillion, roughly equivalent to $7 trillion in premiums. This remarkable growth is set to unlock vast opportunities for China’s insurance market and it’s big players. Ping An, being the leading insurer in China with its comprehensively integrated range of products and services, coupled with its significant and continuously growing customer base, is excellently positioned to capitalize on this unfolding opportunity.
Demographics
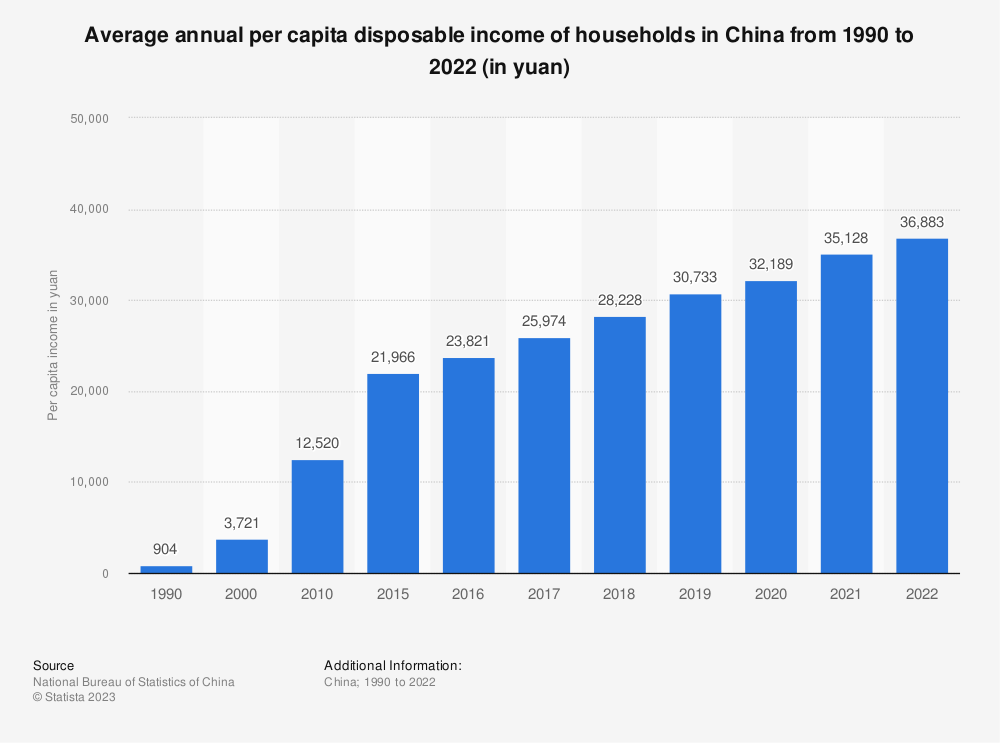
China's vast population and changing demographics play a crucial role in shaping the insurance market. The ongoing urbanization and rising middle class in China has increased disposable income and the ability to invest in insurance products for protection, wealth preservation, and future planning.
According to the data released by the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS) in January 2023, disposable income per capita in China increased by 5% YoY to RMB 36,883 in nominal terms (about $ 5,487) in 2022. After deducting price factors, per capita disposable income rose 2.9 percent from the previous year.
After China’s population growth rate surpassed the world average from 1949 to the late 1970s China, it is now experiencing an aging population, driven by declining birth rates and increasing life expectancy. This demographic shift creates another demand factor for life and health insurance products.
Penetration and Market Size
Despite its extensive population and the growing insurance market in China, the insurance penetration rate, which measures premiums as a percentage of GDP, remains notably lower compared to other developed economies. As per Swiss Re's Sigma report, the insurance penetration rate was approximately 4.5% in 2021. This contrasts with developed markets like the U.S. (6.5%) or Japan (8.2%), underscoring substantial growth potential within the market and present ample opportunities for Ping An to capitalize on.
Another analysis by Deloitte highlights that the disparity between China's insurance market and developed counterparts can be largely attributed to limited product options, underdeveloped sales channels, and historically low insurance awareness. A telling metric, China's average per capita spending on life insurance, referred to as insurance density, paints a vivid picture. In 2019, this figure stood at around $275, standing in stark contrast to developed markets like the United States, where it reached $2000, or Japan, boasting a substantial $9000. This divergence in insurance density not only underscores the existing disparities but also highlights the ample room for growth and expansion within China's insurance sector.
Natural Disaster
The increasing frequency of extreme weather events in China could test the profitability and risk-selection processes of major property and casualty insurers. For example, Heavy rains and floods in the country's Henan province in July 2021, led to a record insurance losses in China, at RMB 12.4 billion for life, property and casualty insurance claims combined.
Competition
The life insurance markets in the Asia Pacific region are highly concentrated, with the top five players holding over 50% of the market share, according to KPMG analysis. Developed markets in the region are typically led by domestic insurers, except for Hong Kong and Singapore, where international players like AIA Group have significant regional presence.

After the booming growth during the COVID-19 pandemic and continuous digitalization to advance, the health industry has experienced a surge in tech companies, introducing disruptive distribution models and intensifying competition. Tech-driven giants like Tencent and Ali Baba have entered the insurance market, offering innovative and technology-driven solutions. This also highlights a reduced entry barrier, particularly for Chinese e-commerce companies that already command substantial traffic in their e-commerce platforms, to step into the market and compete for a slice of the market share.
The role of technology is set to be crucial going forward, and Ping An, with its technological advancements and access to integrated ecosystem of various products and services, is well-positioned to benefit.
In conclusion, the insurance market in China is undergoing significant transformation and expansion. The demographic trends, regulatory environment, penetration levels, and distribution channels all influence the market's dynamics. While challenges exist, the industry's growth prospects remain promising, making China still an attractive destination for both domestic and international insurers.
Financials & Key Figures
So, how does Ping An’s ecosystem benefits it’s operations in number ?
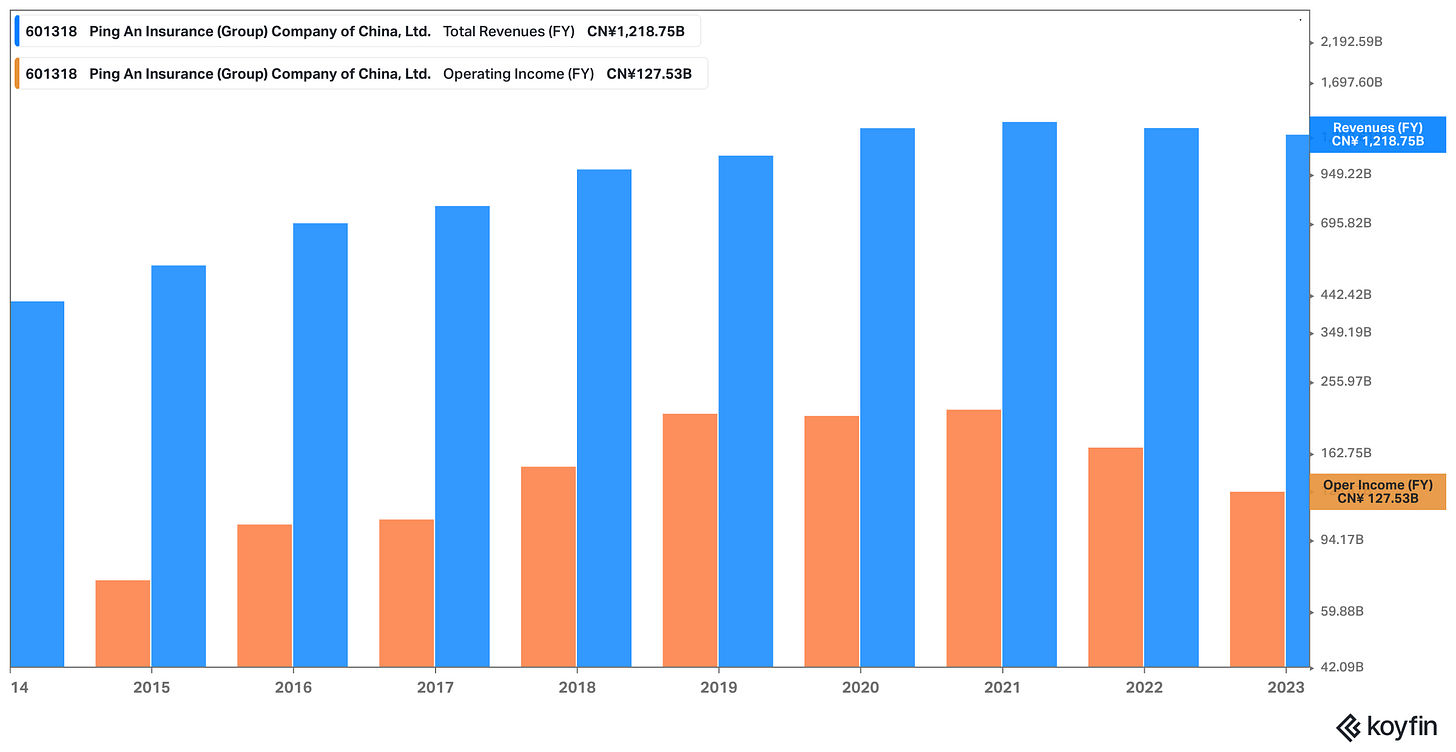
Following its successful IPO in 2004, Ping An has consistently demonstrated robust revenue and profitability expansion. Over the past ten years, the company achieved a 13% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) in revenue.
As a result of this remarkable growth story, it become one of the world's largest financial services companies globally, boasting a market capitalization of RMB 874 billion (equivalent to $122 billion).
Nonetheless, the most recent weakness in consumer demand squeezed by three years of COVID restrictions, have taken their toll. This has led to a 4.2% decrease in total revenue, amounting to RMB 1.28 trillion for the entirety of the year 2022.
The driving force behind the company's modestly enhanced profitability emerged from its life and health insurance segments, alongside its banking operations. These segments witnessed a noteworthy surge in operating profit, with figures rising by 16.0% and 25.3%, respectively. This positive momentum helped offset the declines experienced in other sectors.
Next, delving into Ping An's varied product portfolio and its core business segments provides valuable insights into its historical achievements, prospective growth possibilities, and the interconnected risk factors at play.
Ping An Life
The life and health segment, Ping An’s bread-and-butter business, showed a consistent 16.4% annual growth in operating profit, reaching RMB 111,235 million in 2022.
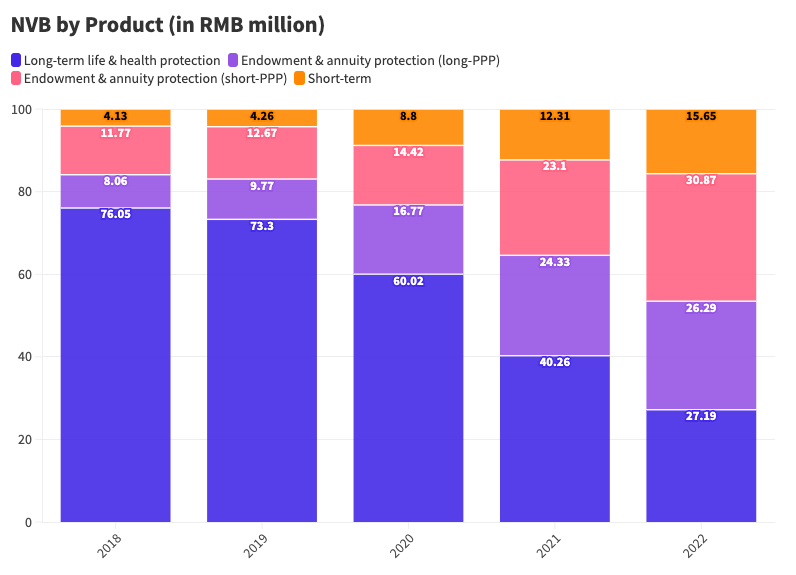
However, the impacts of the Covid-19 pandemic and general consumption weakness had a notable effect on the new business value (NBV), which represents the value of newly sold insurance premiums within a certain period. This impact was particularly pronounced within the agency channel, primarily due to operational constraints stemming from face-to-face visit restrictions. As a result, Ping An's life and health business witnessed a decline of 24% in NBV, settling at RMB 28.8 billion. This decline extends the trend of decrease that began in 2020, indicating the lingering influence of pandemic-related challenges on the company's performance within this segment.
The decrease of the higher contribution from high-margin products, specifically long-term life and health protection, exerted a more substantial impact on the NBV. These products had previously constituted 70% of the NBV prior to the pandemic, making their decline particularly significant.
Although not yet fully back to its pre-pandemic levels, Ping An's NBV within the agent channel exhibited a notable resurgence and shifted into positive growth during the first quarter of 2023. This signals a clear and significant recovery since the challenges experienced in 2020, propelling Ping An back on the path of growth in its most important and profitable business segment.
As part of a quality-focused three-year business reform, Ping An initiated an effort to drive digital transformation and enhance the efficiency of its life insurance agent force structure. The reform included a strategic reduction of low-productivity agents and a departure from the conventional "mass in, mass out" agent development approach. As a tangible outcome of this transformative strategy, there was a sustained reduction in the size of Ping An's individual life insurance sales force, witnessing a significant decrease of 25.8% to a total of 445,000 agents. This transformative shift underlines the company's commitment to elevating performance standards and optimizing its operational framework for improved results.
The reduction in the number of life insurance agents had notable repercussions on business operations, playing a role in the decrease of NBV. The reform, initiated in 2020, also addressed the external challenge, particularly heightened competition stemming from global tech giants like Tencent and Alibaba. These industry leaders extended their influence from social media and e-commerce into the realms of banking and health sectors, thereby intensifying the competitive environment.
Of significant importance, as a result of this comprehensive three-year reform undertaken amidst a backdrop of challenges, Ping An has witnessed an enhancement in both product and business quality.
As a result of this three-year reform, amidst the challenges, Ping An has witnessed an enhancement in both product and business quality. The NBV per agent experienced a noteworthy 22.1% YoY surge, reaching RMB 47,630 in 2022, even as total NBV was down in the double digits during the same time period.
Ping An P&C
This segment of the business is mainly driven by premium income from Auto Insurance, accounting for nearly 70% of total revenue, along with non-insurance (such as property, travel) and accident & health insurance. At the end of 2022, total premium income from P&C increased by 10.4% YoY to RMB 298,038 million while operating profit before tax dropped by 56% to RMB 8,23 million during the same period.
The decline in operating profit within the P&C segment can be primarily attributed to two factors. Firstly, there was an underwriting loss of RMB 888 million by the end of 2022, which points to increased losses due to a surge in claims and disproportionate expenses. This suggests that the claims paid out exceeded projections, while the collected premiums fell short of covering overall costs. These losses are specifically linked to the guarantee insurance business and were amplified by the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, according to the company's assessment.
Additionally, the weakening underwriting performance of Ping An P&C is evident in the reported combined ratio of 100.3% for 2022. A combined ratio above 100% indicates a loss, signifying that the net premium income fell short of covering net insurance claims and expenses, resulting in underwriting losses.
It’s worth noting that, for the second time since 2004 (with the initial occurrence in 2008), the combined ratio has exceeded 100%. From 2004 to 2022, the company maintained an average combined ratio of 96.8%. In comparison, an Ernst & Young (E&Y) study in 2020 on USD Property & Casualty (P&C) Insurance revealed an industry average of approximately 100.6%.
The second factor affecting the operating profitability of the P&C segment in 2022 was the drop in investment yield for the average investment assets, which stood at 2.8% at the end of 2022, down from 4.3% the previous year. This decline was primarily attributed to the turbulent domestic and international environment, leading to instability in capital markets, as well as historically low domestic bond yields.
Despite the difficulties faced in the past year, Ping An's Property and Casualty (P&C) remained the second-largest P&C insurance company in China and with the ongoing recovery of China's economy, promising opportunities within the P&C insurance business segment, such as property, auto, and travel insurance, are poised for growth.
Ping An Banking
It's banking segment saw a 6.2% YoY revenue increase to RMB 179,895 million and a 25.6% YoY net profit increase to RMB 36,34 million in 2022. The retail asset under management (AUM) continued to rose 34.3% from the beginning of 2022 to exceed RMB 1 trillion as of end of 2022, signalling strong growth for the banking segment of Ping An.
From a regulatory perspective, Ping An Bank's financial strength, as indicated by the core tier 1 capital adequacy ratio, reached 8.64% by the end of 2022. Notably, the core tier 1 capital adequacy ratio remains above the minimum regulatory requirements of 7.5%.
Ping An Asset Management
Ping An’s Asset Management business demonstrated consistent business expansion. The AUM increased by 7.8% from the start of 2022, reaching RMB 4.37 trillion (equivalent to about $600 billion based on current exchange rates) by the end of 2022.
In light of China's real estate challenges in 2021, which notably affected Ping An through considerable losses linked to the real estate developer China Fortune Land Development, the company took action by decreasing its exposure to real estate developers. Real estate holdings comprised 4.7% Ping An's total assets at the end of 2022, which stood at RMB 4.37 trillion, and approximately 60% of this allocation was directed towards physical buildings, reflecting a 10% growth from the corresponding figure two years prior.
Operating Efficiency & Profitability
In 2022, Ping An witnessed a decline in its operating return on equity (ROE), which settled at 18%, primarily attributed to the impact by the pandemic.
Ping An's high ROE is propelled by its strategic investments in technology, fostering synergies with core operations. Moreover, Ping An's L&H segment, which constitutes the majority of the operating profit, exhibits an impressive ROE of 32.7%. This approach not only enhances returns but also amplifies growth prospects, setting Ping An at the forefront compared to its peers.
Strong financial position and low bankruptcy risk
Aligned with the China Risk Oriented Solvency System (C-ROSS) Phase II regulation, introduced by the Chinese regulators in January 2022, Ping An showed strong financial resilience. The group's comprehensive solvency margin ratio, which gauges the actual capital in relation to the minimum capital requirement, reached 218%. Additionally, the core solvency margin ratio, which assesses core capital against the minimum capital requirement, reached 166%. These figures underline that Ping An possessed ample capital well above minimum capital requirement, indicating low risk of bankruptcy.
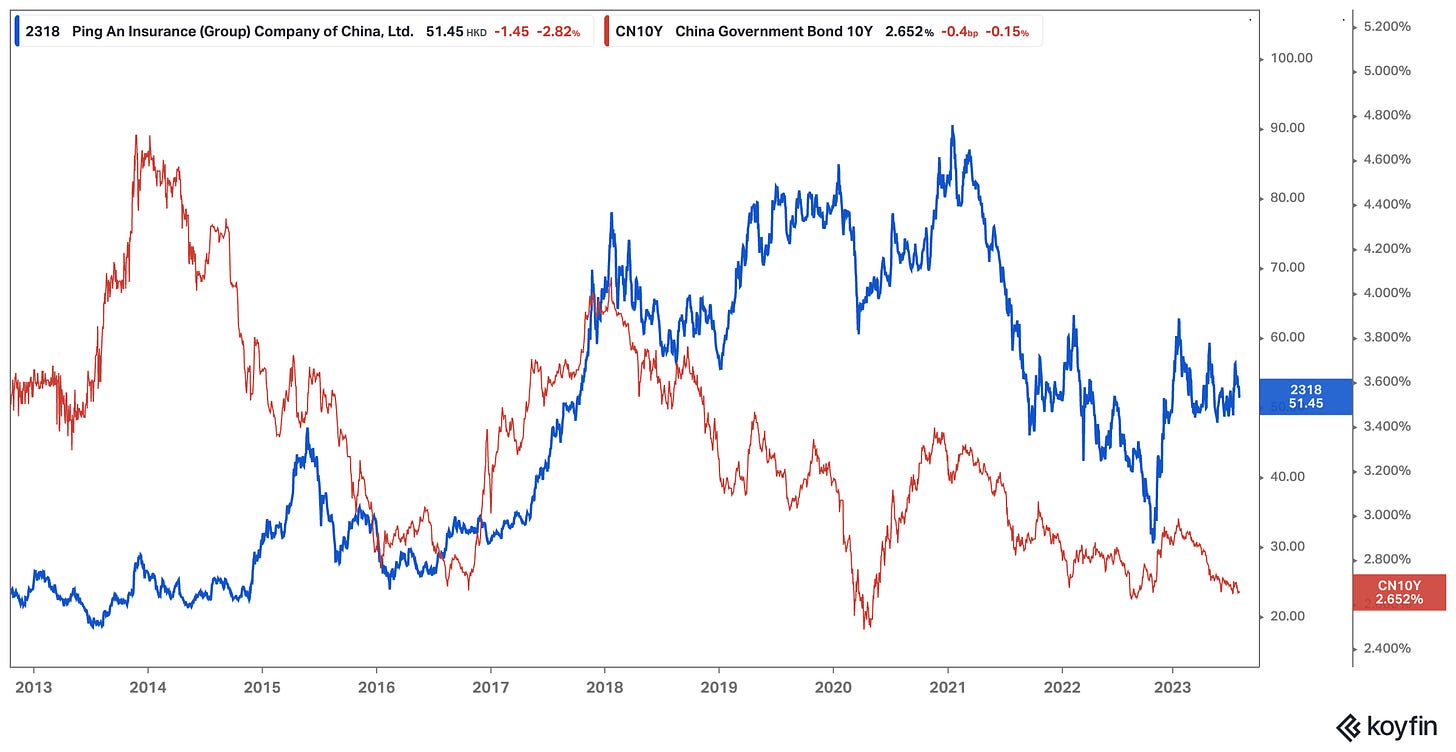
A notable risk to Ping An's life insurance business segment involves the potential fluctuations in long-term interest rates. A decline in interest rates could lead to reduced returns on their investments, subsequently exerting downward pressure on overall profitability and adversely affecting Ping An's stock price (like in 2015/16 and 2017/18).
Dividend
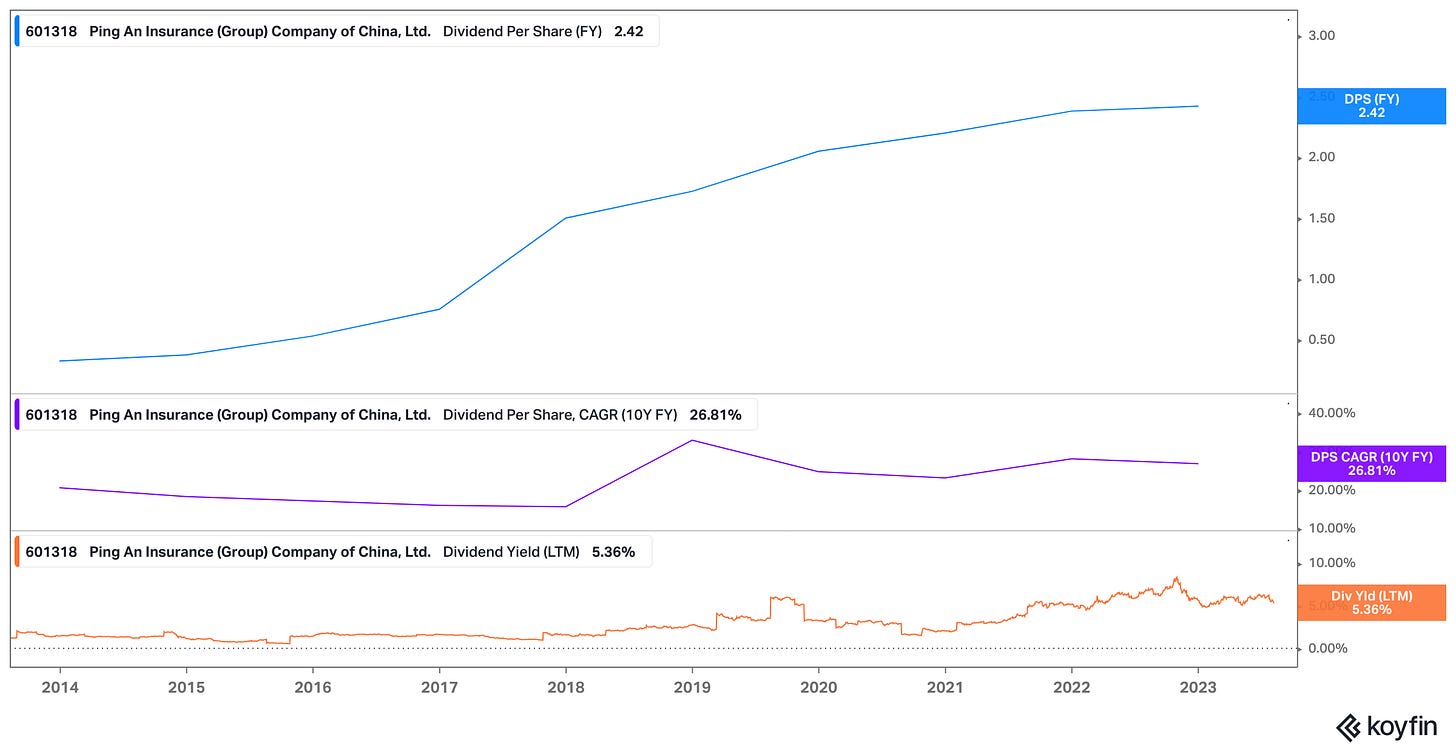
Ping An sustained its dividend growth trend, raising by 1.7% YoY in 2022 and delivering a full-year cash dividend of RMB 2.42 per share. The company maintained its consistent average dividend payout ratio of 30%, calculated from operating profit attributable to the parent company's shareholders (excluding share repurchases). In terms of dividend growth, Ping An achieved a remarkable ten-year CAGR of 26%.
Shareholder
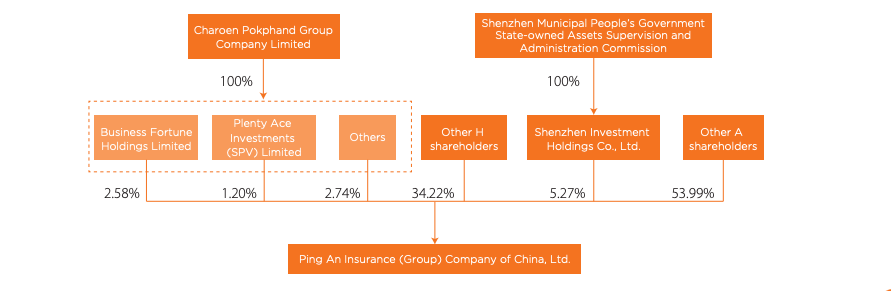
Ping An has a relatively fragmented structure with no controlling shareholder. As of December 2022, significant stakeholders, each holding 5% or more equity stake, encompass Charoen Pokphand Group Co., Ltd., possessing 6.52%, and Shenzhen Investment Holdings Co., Ltd. (a state-owned capital investment firm) owning 5.27%.
Outlook
Ping An's strong track record and high-quality business, integrated healthcare and financial service ecosystem, along with the rebound in rising total NBV in Q1 2023, it is strategically positioned to reassert itself and leverage the advantageous demographic landscape and the rising awareness and need for healthcare in China.
Bull and Bear Investment Case
Bull Case
Ping An Life's ongoing three-year reform drive to strengthen its agent force, coupled with cross-selling potential within its advanced ecosystem, forms a compelling bull case, promising new business value growth, enhanced profitability
China’s insurance market remains underserved due to the aging population and a middle class with low insurance penetration and density rates compared to other developing countries and is projected to experience substantial growth and increased valuation in the future
Rising awareness of personal risks has marked recent years and Ping An with its health ecosystem is well positioned to provide more comprehensive and individualised products, aiding customers in managing challenges linked to longevity and health risks
Bear Case
In a low interest rate environment, the insurance industry faces difficulties, with interest rate cuts leading to reduced profitability and lower company valuations, exacerbated by the narrowing spread between investment returns and policyholder payouts.
Despite the optimistic prospects surrounding the growing middle class in China and other developing countries such as India and Southeast Asia, realizing the full potential of these opportunities may prove challenging due to intensifying geopolitical risks and recent concerns
With more frequent and severe weather events, like the severe flooding in China’s Henan province in 2021, insurers could face a surge in claims, leading to straining profitability, diminished premium growth and overall investment uncertainty for the industry
Regulatory uncertainty in China like the real estate crackdown, auto industry reforms, and Ping An's role in the bankruptcy restructuring package for Founder Group (a state-owned conglomerate linked to Peking University) might hinder Ping An’s ability to achieve its desired growth trajectory and maintain profitability
Valuation
Ping An’s H-shares are currently trading at historically low valuation levels, with a price-to-book (P/B) ratio around 1x, below the 10-year average of 1.9x, and a price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio of 9.4x.
At the current valuations, a return to the average historical P/B ratio of 1.9x, represents an almost 100% upside at the present moment (even without considering the 5% dividend yield based on today's share price).
Peer Valuation
Which Chinese insurer holds the most promising investment potential? Among the five largest insurers in China based on market capitalization, PICC and New China Life Insurance offer particularly attractive valuations compared to todays domestic industry average P/B of 1.5x.
With a solid group level ROE of 18% in 2022, and an even more remarkable ROE of 32-35% within its Life & Health insurance segment, coupled with its technology-driven integrated ecosystem, Ping An stands out as an appealing business with substantial growth potential.
To put the valuation of the overall market into perspective, especially when including international peers like China Life, Allianz SE, Elevance Health, the industry's average P/B ratio increases to 2.3x. This underscores the significant undervaluation of the Chinese insurance sector at present.
Final thoughts
Now, one might ask: Is this an opportune time to consider adding Chinese insurers to the portfolio?
Given Ping An’s dominant position in China’s insurance and health industry, and currently depressed valuations, it emerges as the more promising insurance business compared to peers. This assessment holds true even on a global scale, given the undervaluation of the entire Chinese insurance industry.
However, recent developments, including the real estate crackdown, reforms in the auto industry, and the ongoing geopolitical tensions have revealed certain investment risks into China. Amidst these challenges, I believe that Ping An presents a compelling risk-reward ratio.
Disclaimer: This publication and its authors are not licensed investment professionals. The information provided in this publication is for educational purposes only and should not be construed as investment advice. We do not make any recommendations regarding the suitability of particular investments. Before making any investment decision, it is important to do your own research. RhinoInsight assume no liability for any investment decisions made based on the information provided in this newsletter.
Reference:
Company Website Investor Relations
https://group.pingan.com/investor_relations.htmlAnnual Report 2022
https://group.pingan.com/resource/pingan/IR-Docs/2023/pingan-ar22-presentation.pdfAllianz Global Insurance Report 2023 www.allianz.com/content/dam/onemarketing/azcom/Allianz_com/economic-research/publications/specials/en/2023/may/2023_05_17_Insurance-Report_AZ.pdf
REPORT: CHINA’S LIFE INSURANCE PREMIUM TO SURPASS THE US MARKET BY 2030 AND REACH 45 TRILLION YUAN BY 2050 https://www.oliverwyman.com/media-center/2022/mar/report-chinas-life-insurance-premium-to-surpass-the-us-market-by-2030-and-reach-45-trillion-yuan-by-2050.html
UNLOCKING THE 45 TRILLION YUAN POTENTIAL https://www.oliverwyman.com/our-expertise/insights/2022/mar/unlocking-the-45-trillion-yuan-potential.html
Swiss RE: World Insurance (Nov 4/2022)
https://www.swissre.com/dam/jcr:4500fe30-7d7b-4bc7-b217-085d7d87a35b/swiss-re-institute-sigma-4-2022.pdf
Further Readings:
Reader question: Ping An Insurance? by Michael Fritzell (Asian Century Stocks)
https://www.asiancenturystocks.com/p/pinga
McKinsey-Interview with Jessica Tan (Co-CEO and key architect of Ping An’s digital-ecosystem-based business model)
Jessica-Tan on the Chinese giant’s transformation from insurance to technology
Building an insurance ecosystem: Lessons from the PingAn Story with Jonathan Larsen’s (CIO at Ping An)